- Ministry of Cultural Heritage and Activities
- Directorate General for Books and Cultural Institutes - Rome
- University of Naples Federico II
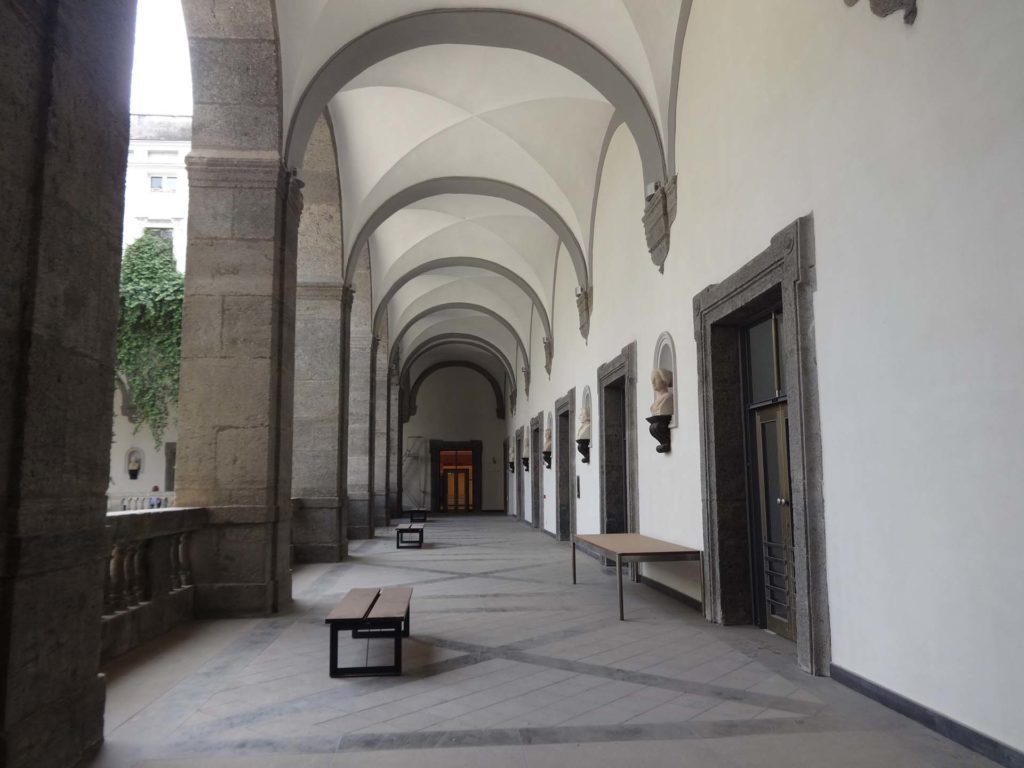
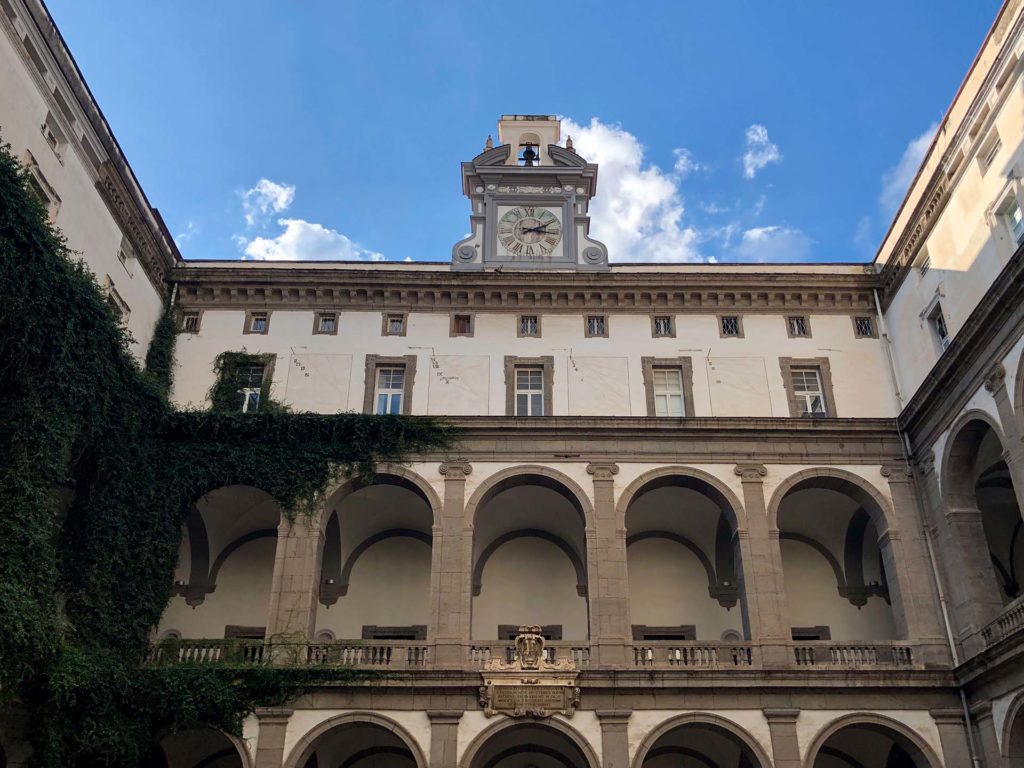
University Library of Naples and Statue Courtyard - Naples
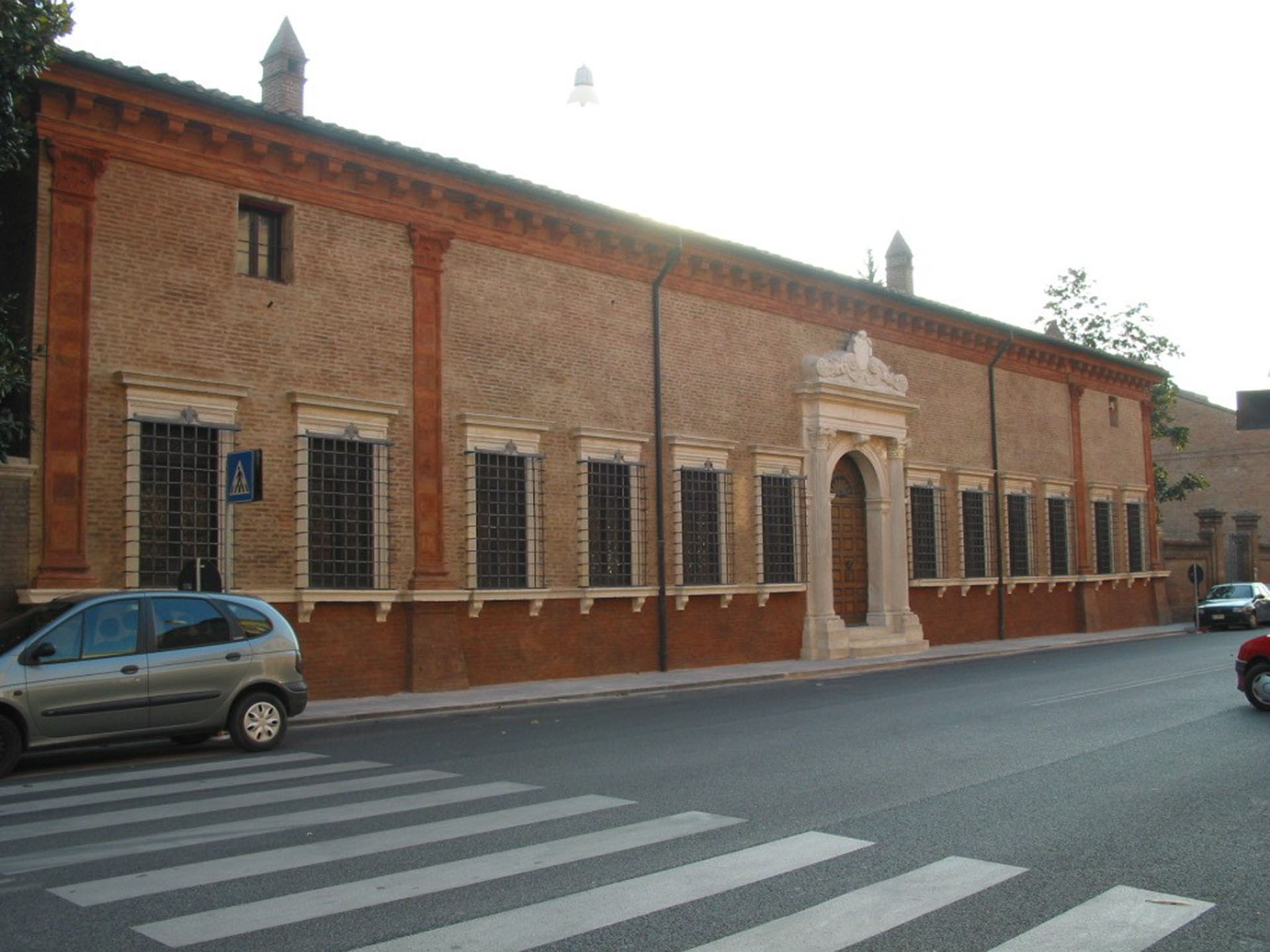
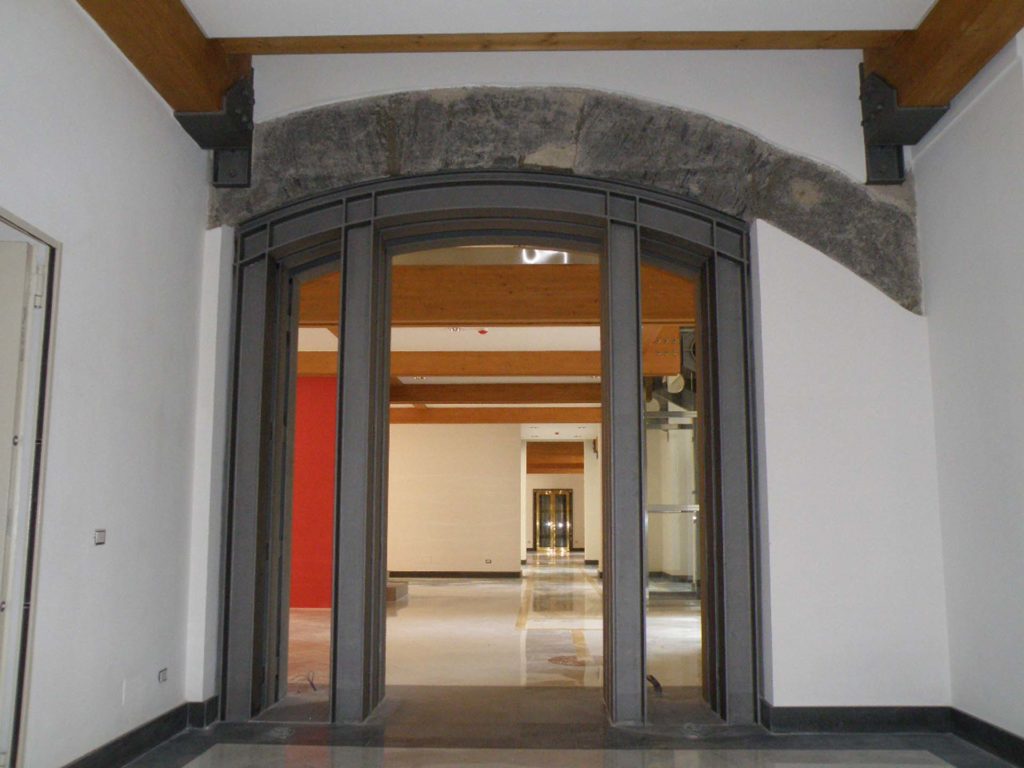
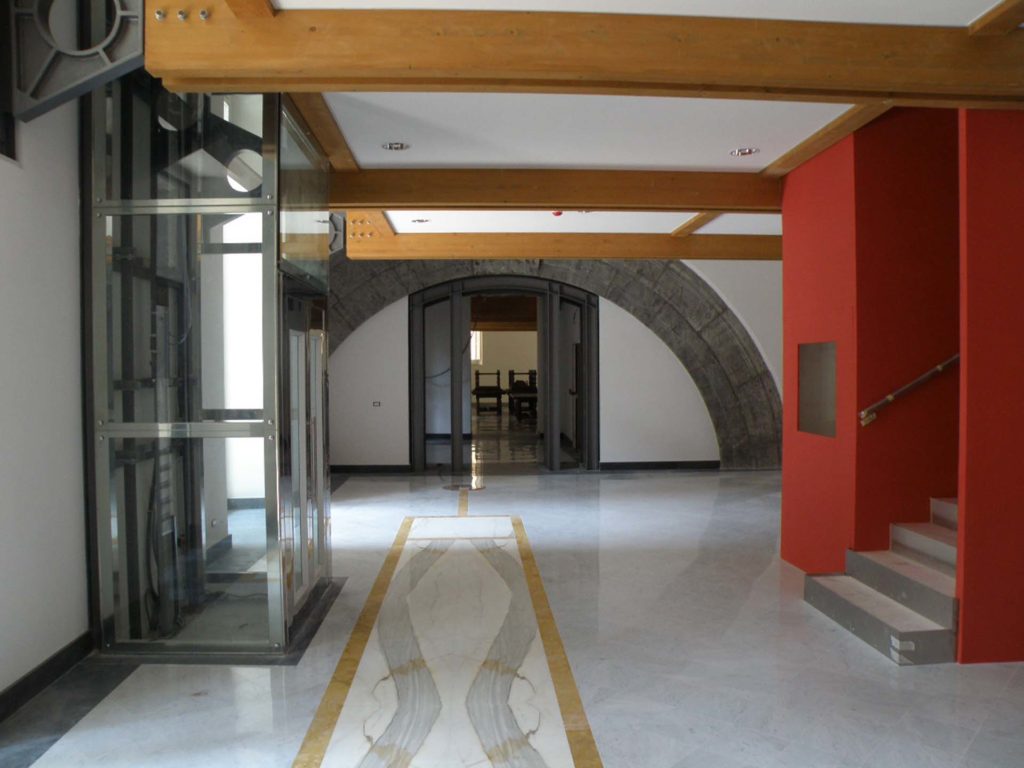
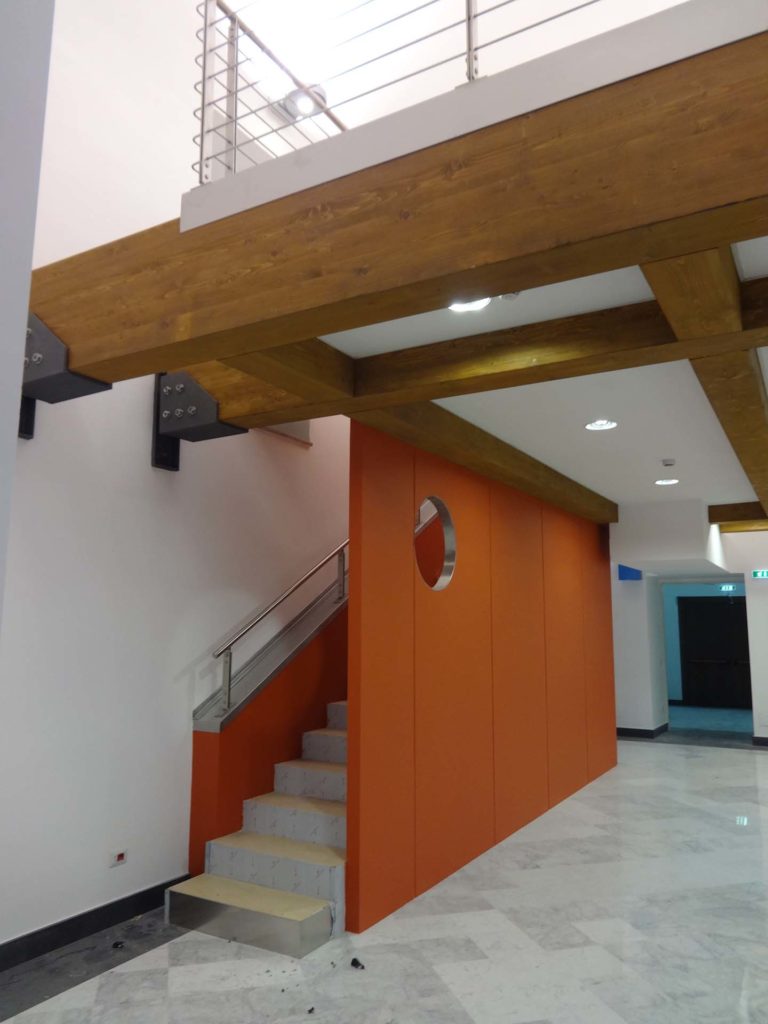
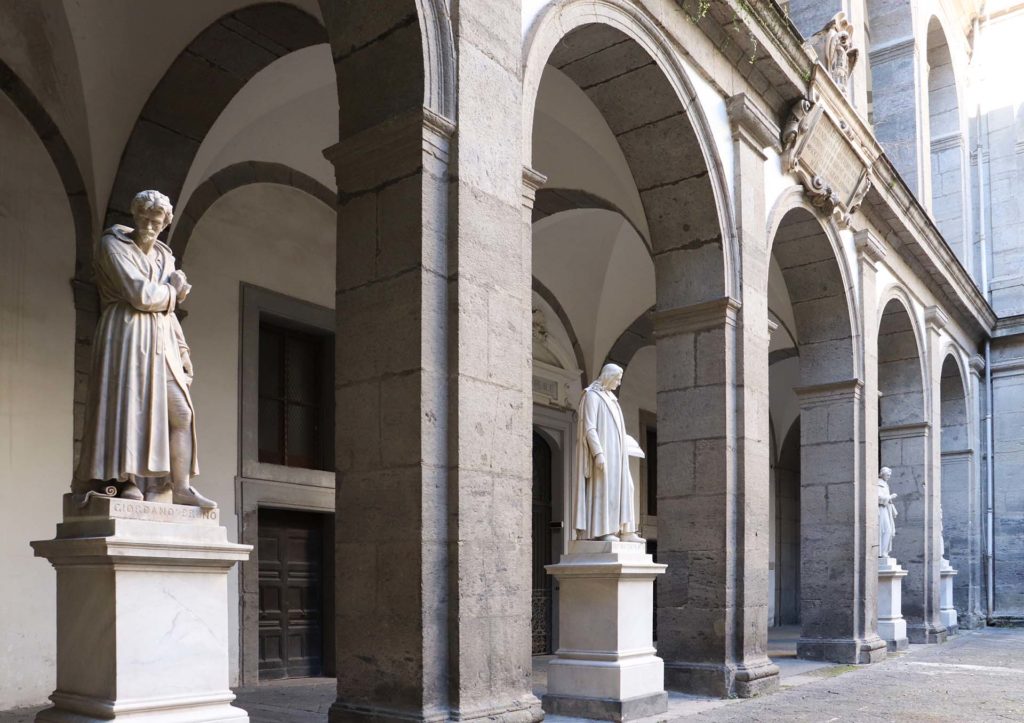
The University Library of Naples (BUN) is a state public library dependent on the Ministry of Culture; is located in Via Giovanni Paladino n.39 and is located in the former Collegio Massimo that was renamed Casa del Salvatore when Ferdinand IV expelled the Jesuits from the Kingdom of Naples. The complex, founded by the Jesuits consists of two buildings articulated around two courtyards: the seventeenth-century Monumental Courtyard (called Courtyard of the Statues) and the eighteenth-century Courtyard of the Saviour. Both the church and the courtyard were demolished and incorporated into the subsequent structures built in the seventeenth century. In the eighteenth century, on the body of the factory at the entrance and on the opposite, were added two floors of rooms leaving the other two sides uncovered: these two terraces were then covered and transformed into classrooms during the thirties of the twentieth century.
In 1768 the College was renamed Casa Adel Salvatore and the Boarding School was established there. In 1777 it was decided that the University, housed until then in the current National Archaeological Museum, moved to the headquarters of the Real Casa del Salvatore, which has since become the historic seat of the University of Naples. Because of the events related to the Neapolitan Revolution of 1799, the College of the Savior interrupted its activity and was in part intended as a hospital for Russian troops. In 1805 the College reopened and in 1812 was elevated to the rank of Lyceum but ended its activity in 1860.
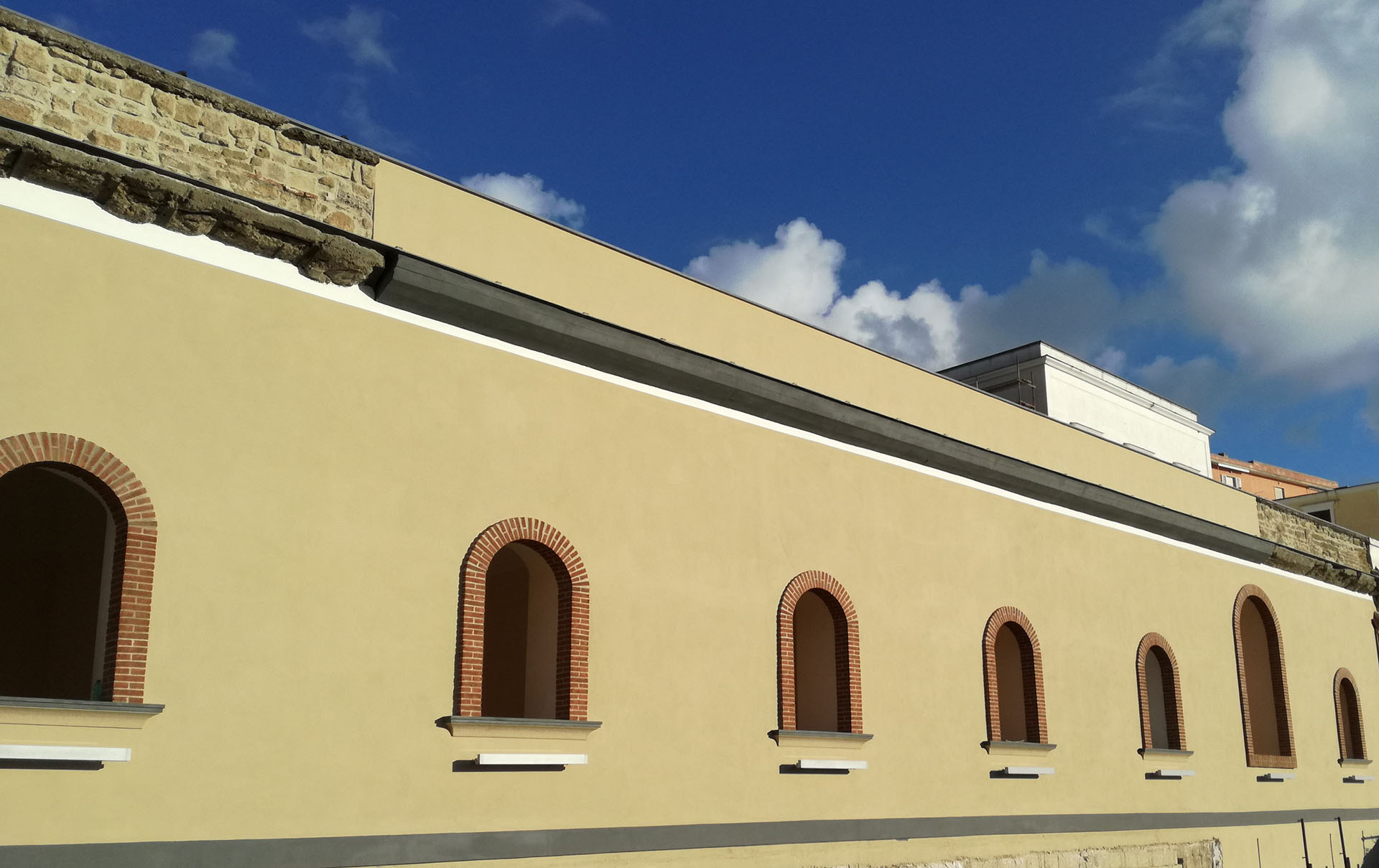
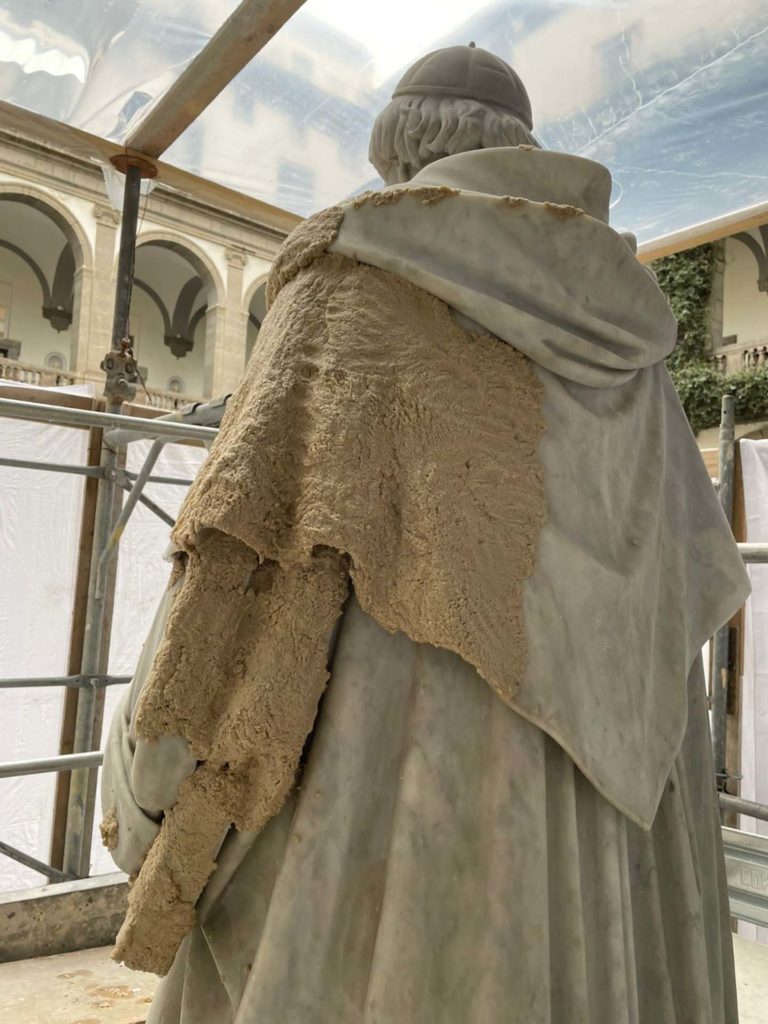
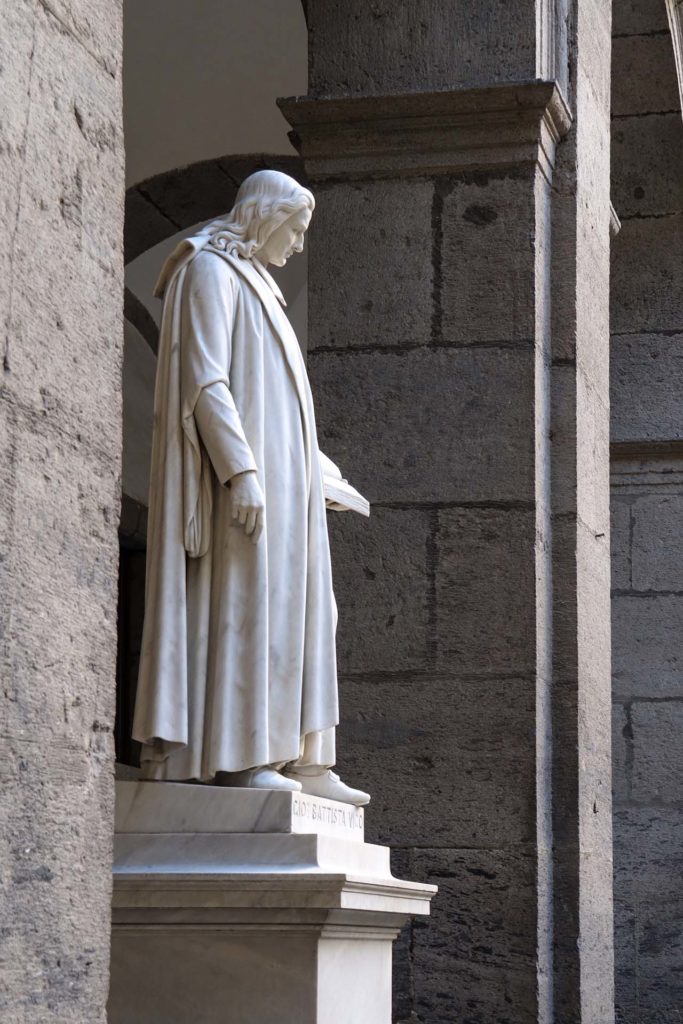
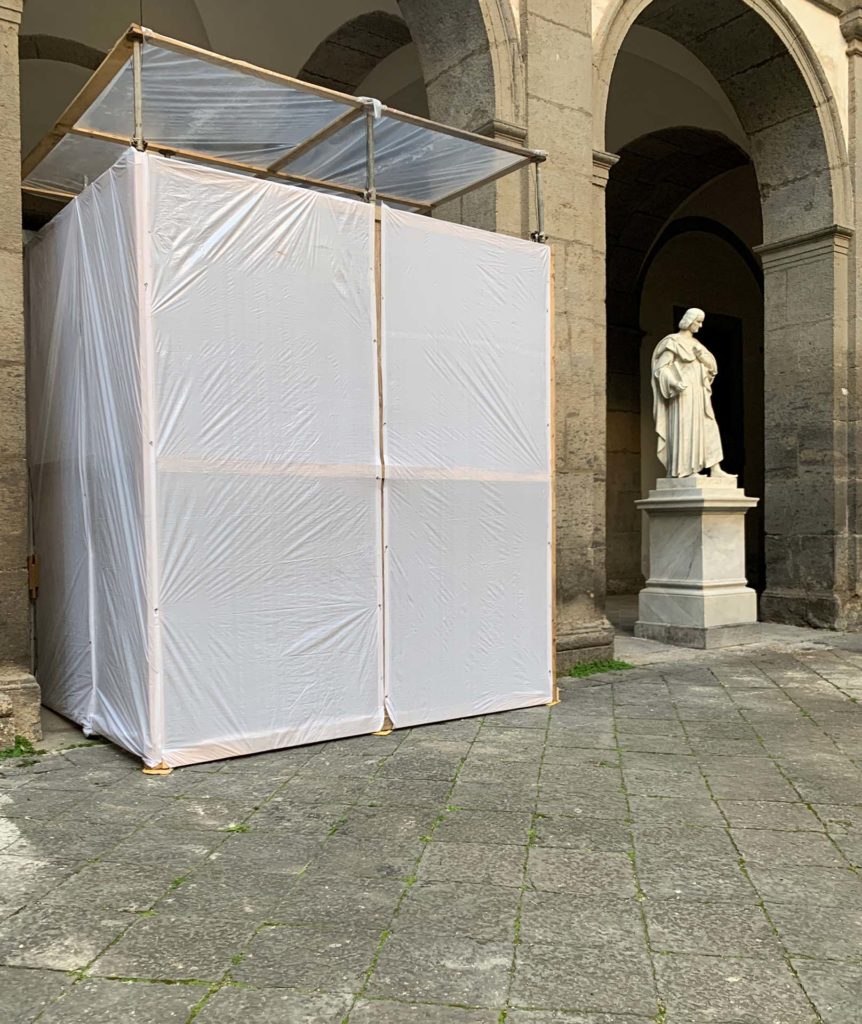
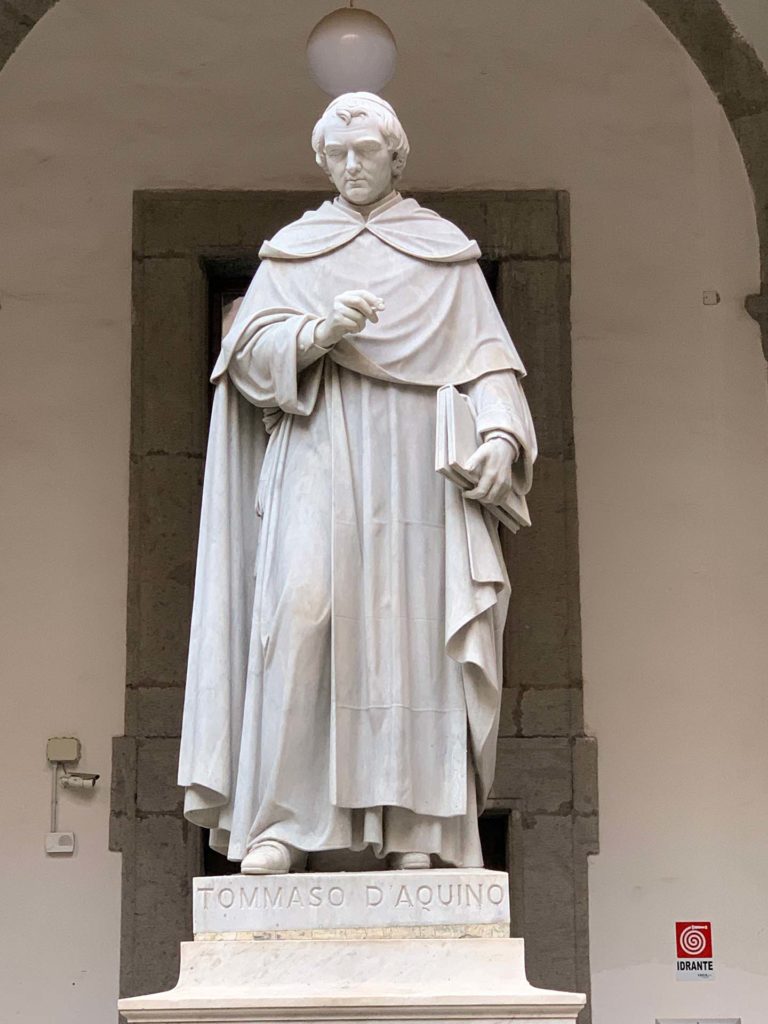
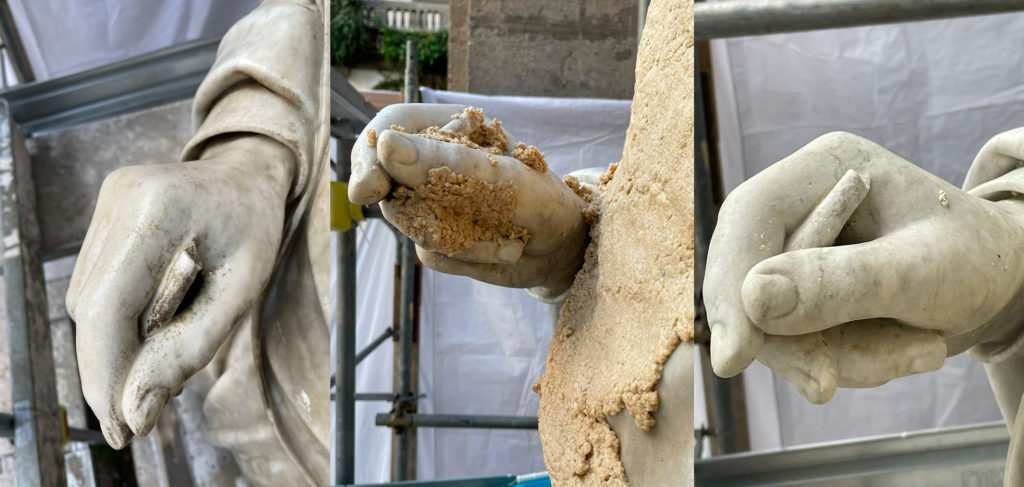
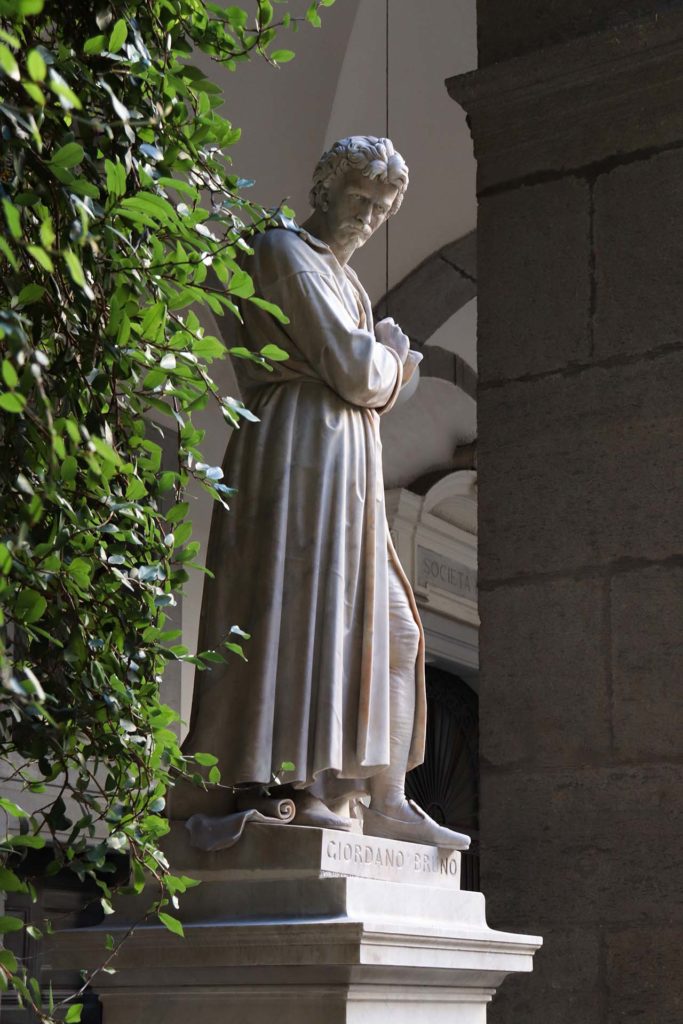
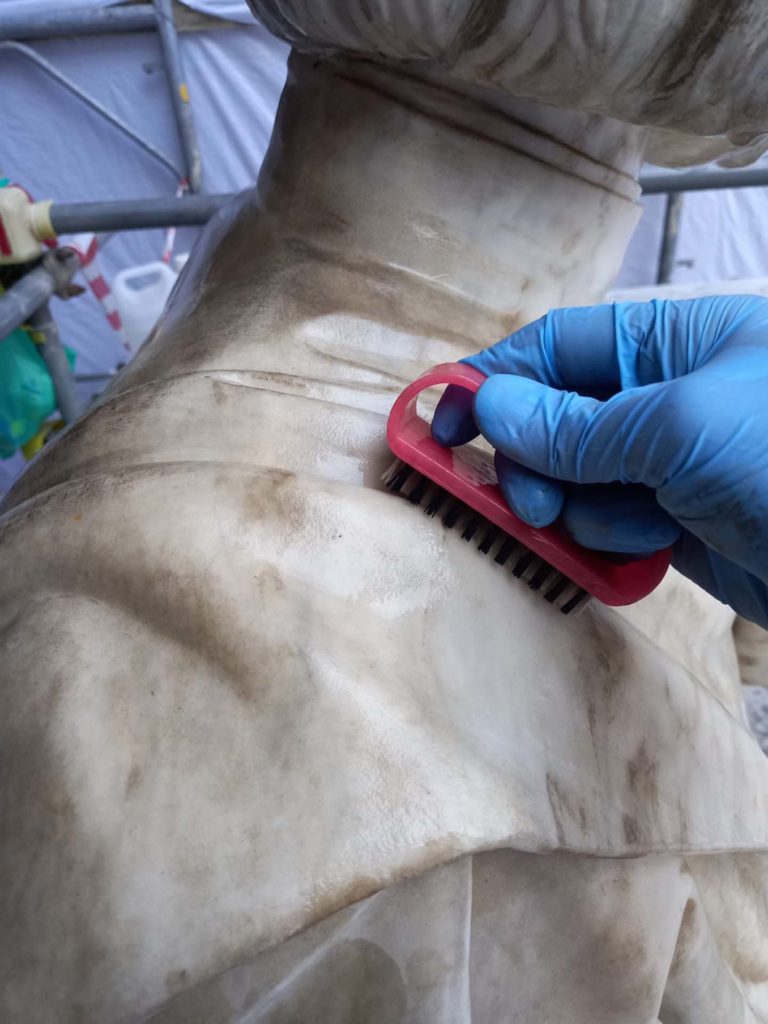
The intervention aims to focus on the preservation of "Renaissance" forms of the work, through technologically advanced solutions for the conservation and maintenance of volumes, better redistribution and optimization of spaces and greater storage of volumes. In addition, the planned interventions for the four statues of the Marble Courtyard: P. Masulli, Giordano Bruno, Pier Delle Vigne and Giambattista Vico, have the aim of giving an overall reading of the works. The works involved cleaning operations, the accurate removal of existing grouting not compatible with the support and the consolidation of the stone elements in order to strengthen and stabilize the structure. The restoration of the statues ends with the compensation of the deficiencies and the relocation of the removed elements with the aim of restoring the readability of the four works.